Exploring British and American Cultures
Exploring the Rich Tapestry of American Food Culture
Nguyễn Phương Thùy
Lớp D11.20.02
The food culture of America is a melting pot of many different cultures, each one bringing their own culinary traditions. Owing to immigration to America from a wide range of different cultures, American cuisine is also a product of diversity. The country has a high consumption of meats, including chicken, pork, and lamb. Potatoes, green vegetables, and sweet breads also feature heavily in American cuisine. In addition, the local, seasonal, and sustainable food movement has taken hold across the country, with farmers’ markets popping up in many neighborhoods and farm-to-table restaurants showcasing produce, meat, and dairy from nearby farms. However, fast food chains are also popular in America, with fast food, along with pop music and jeans, being one of America’s biggest “cultural exports”.

Fast food in US
- Historical Evolution of Fast Food
Emergence of Fast Food Concepts Automobile Culture in the Early 20th Century and the rise of automobile culture in the early 20th century played a crucial role in the development of fast food. Drive-in restaurants and roadside diners became popular, providing quick meals for travelers.

White Castle (1921)
Often credited as the first fast-food chain, White Castle, founded in 1921 in Wichita, Kansas, introduced the concept of standardized food production using industrial techniques. They focused on cleanliness and consistency.
McDonald’s and Fast Food Chains McDonald’s (1950s)
The real explosion of fast food came with the establishment of McDonald’s by Ray Kroc. He transformed the original McDonald’s restaurant, founded by Richard and Maurice McDonald in San Bernardino, California, into a franchise model. The Speeded Service System emphasized efficiency and consistency.
Franchising Model

McDonald’s success popularized the franchising model in the fast-food industry. Other chains like Burger King (1954) and Taco Bell (1962) followed suit, expanding the reach of fast food across the country.
Fast Food Culture Takes Hold Cultural Impact
Fast food became deeply embedded in American culture during the 1960s and 1970s. It symbolized the modern, fast-paced lifestyle of post-war America.
Expansion and Diversification: Fast-food chains expanded their menus to include a variety of options. McDonald’s introduced the Big Mac in 1968, and pizza chains like Domino’s and Pizza Hut gained popularity.
Globalization and Health Concerns Global Expansion
Fast-food chains went global, spreading American fast-food culture worldwide. McDonald’s became an international icon, adapting menus to local tastes in different countries.

Health Concerns
The 1980s and 1990s saw growing concerns about the health implications of fast food, particularly regarding obesity and dietary issues. This led to increased scrutiny and calls for healthier options.
Health Consciousness and Evolution Healthier Alternatives
Fast-food chains responded to health concerns by introducing healthier menu options, such as salads and grilled items. Some chains also pledged to eliminate trans fats from their products.
Technology Integration
The 21st century saw increased use of technology in fast-food services, including online ordering, mobile apps, and delivery services, adapting to changing consumer habits.
Current Trends – Sustainability and Cultural Diversity Sustainability
Modern consumers are increasingly concerned about sustainability and ethical sourcing. Fast-food chains are responding by incorporating more sustainable and locally sourced ingredients. Cultural Diversity: There is a growing emphasis on cultural diversity in fast-food offerings, with chains incorporating international flavors and catering to diverse dietary preferences.
The history of fast food in America is marked by innovation, cultural impact, and adaptation to societal changes. It continues to evolve, influenced by health considerations, technology, and the ever-changing tastes of consumers.
- Key Characteristics of American Fast Food Culture
American fast food culture is characterized by several key features that have contributed to its widespread popularity and influence. These characteristics reflect the unique aspects of the fast food experience in the United States.

Speed and Convenience
Fast food is designed for quick service and on-the-go consumption. Speed and convenience are paramount, with most transactions focused on getting customers their meals as quickly as possible.
Standardization
Standardization of recipes and processes ensures consistency across different locations of a fast-food chain. This contributes to a uniform dining experience, regardless of the specific outlet.

Franchising
The fast-food industry is heavily reliant on the franchising model. Major chains, such as McDonald’s, Burger King, and Subway, have expanded rapidly by offering franchise opportunities to entrepreneurs, contributing to the ubiquity of these brands.

Marketing and Branding
Strong marketing and branding are integral to American fast food culture. Recognizable logos, slogans, and advertising campaigns play a crucial role in building and maintaining brand loyalty.
Menu Innovation
Fast-food menus are known for their innovation and adaptability. Chains constantly introduce new items, promotions, and limited-time offerings to keep customers interested and attract new ones.
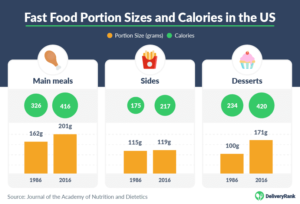
Portion Sizes
American fast food is often associated with large portion sizes. “Supersizing” became a trend, offering customers larger servings of fries and drinks. This aspect has been a subject of discussion related to health and nutrition.
Drive-Thru Culture
The drive-thru has become a defining feature of American fast food. Many chains prioritize drive-thru service, allowing customers to quickly order and receive their meals without leaving their card

Cultural Adaptation
Fast-food menus often adapt to local tastes while maintaining core offerings. In the U.S., this might involve introducing items like the “McRib” or regional specialties to cater to specific preferences.
Youth and Family Focus
Fast food has traditionally been associated with family outings and youth culture. Kid-friendly meals, playgrounds, and promotions targeting children and teenagers contribute to the family-oriented aspect of American fast food.
Globalization
American fast food has been a significant cultural export, leading to globalization of fast-food chains. McDonald’s, in particular, has become an international symbol of American fast food, adapting menus to suit local tastes in various countries.
Iconic Menu Items
Certain menu items have become iconic and synonymous with American fast food, such as the Big Mac, Whopper, or the classic American cheeseburger. These items often serve as cultural symbols.
Controversies and Health Concerns
American fast food has faced scrutiny due to concerns about its impact on health, particularly regarding high-calorie content, trans fats, and the association with obesity. This has led to efforts by some chains to offer healthier alternatives and disclose nutritional information.
American fast food culture is dynamic, adapting to changing consumer preferences and societal trends. While it continues to be a significant aspect of American dining habits, there is also an increasing awareness and demand for healthier and more sustainable options.
- Cultural Iconography of Fast Food
Fast Food as a Symbol of American Culture and Lifestyle
Symbol of Modernity: Fast food is emblematic of America’s fast-paced lifestyle, reflecting the need for quick, convenient, and efficient solutions in daily life.
Cultural Export
The global prevalence of American fast-food chains like McDonald’s and KFC makes them ambassadors of American culture worldwide. Icon of Capitalism: Fast food is often associated with American capitalism, representing mass production, consumerism, and the commodification of food.
Representation in Popular Media and Entertainment
Movies and Television Shows: Fast food is a recurring element in popular media, featured in films like “Super Size Me” and sitcoms such as “Seinfeld,” contributing to its cultural presence. Advertising Dominance
Fast-food commercials, with their catchy jingles and memorable slogans, permeate television, radio, and online platforms, shaping perceptions and creating lasting brand associations. Social Media Influence: The rise of social media platforms has given fast food a new dimension, with influencers showcasing meals, challenges, and reviews, further embedding it in contemporary culture.
Shift in Dietary Norms
Fast food has played a pivotal role in reshaping dietary norms, contributing to a preference for quick, processed, and often high-calorie meals.
Impact on Family Dynamics
Fast-food establishments, with their emphasis on family-friendly environments, have influenced the way families dine out and spend leisure time together.
Convenience Culture
The rise of fast food has contributed to a broader culture of convenience, where time-saving solutions and on-the-go consumption are prioritized.
Changing Perceptions of Food
Fast food has challenged traditional notions of what constitutes a meal, fostering a culture where snacks and quick bites are considered acceptable substitutes for conventional meals.
- Challenges and Opportunities

Generation
Fast food contributes significantly to single-use packaging and food waste, leading to environmental degradation. Addressing this issue involves rethinking packaging materials and waste management strategies.
Carbon Footprint
The production, transportation, and disposal of fast-food items contribute to a considerable carbon footprint. Efforts to reduce emissions can involve sourcing locally, promoting plant-based options, and optimizing transportation logistics.
Water Usage
The production of ingredients, especially meat, in the fast food industry often requires substantial water resources. Sustainable water management practices can mitigate environmental impact.
Animal Welfare
The industrial-scale production of meat for fast food has raised ethical concerns regarding animal welfare. Adopting humane farming practices and offering plant-based alternatives are steps toward addressing this issue.
Fair Labor Practices
The fast-food industry has faced scrutiny for labor practices, including low wages and inadequate working conditions. Ensuring fair wages, benefits, and opportunities for career advancement are ethical imperatives.
Supply Chain Transparency
Ethical considerations extend to supply chain transparency, where consumers demand visibility into sourcing practices to ensure fair treatment of workers and responsible environmental practices.
Opportunities for Sustainability and Positive Change
Plant-Based and Sustainable Options: The growing demand for plant-based alternatives presents an opportunity for fast-food chains to diversify their menus and reduce the environmental impact of meat production.
Local Sourcing
Embracing local sourcing practices supports regional economies, reduces transportation emissions, and enhances the freshness and quality of ingredients.
Fast food culture in the US and the UK
| Fast food culture in the US | Fast food culture in the UK | |
| 1. History and Development | The fast food culture in the U.S. has its roots in the early 20th century but experienced significant growth in the 1950s and 1960s with the emergence of chains like McDonald’s. The U.S. quickly became one of the most diverse and comprehensive fast food cultures globally. | English culinary traditions have deep and enduring roots, influenced by European cuisines and the longstanding cultural heritage of England. Traditional English dishes such as Yorkshire pudding, fish and chips, and steamed puddings are iconic. |
| 2. Food Preparation and Popular Foods | Fast food in the U.S. is often processed on an industrial scale, utilizing pre-packaged ingredients. The U.S. is renowned for fast food staples like hamburgers, pizza, hot dogs, and a variety of other quick-service options. | English cuisine often emphasizes the use of fresh ingredients and on-site preparation. Traditional dishes like Sunday roast, cottage pie, and afternoon tea are highly regarded. |
| 3. International Influence and Cultural Diversity | United States: With the global spread of international fast-food chains like McDonald’s, KFC, and Pizza Hut, the U.S. holds significant influence over global food culture. Fast food menus often incorporate items from various international cuisines. | England: England maintains its uniqueness in its culinary offerings, with a focus on traditional dishes and pride in the cultural diversity within its cuisine, from European-inspired dishes to those from International Heritage. |
| 4. Production Standards and Dietary Norms | Fast food in the U.S. emphasizes convenience, with a diverse menu to cater to quick and varied tastes. Standardization is key to maintaining quality and reducing production costs. | Quality and sourcing of ingredients are highly valued in English cuisine. Culinary standards often demand meticulous preparation and creativity in combining ingredients. |
| 5. Consumer Perception and Attitudes | Fast food in the U.S. is often viewed as a convenient and popular choice. Consumers typically evaluate it based on speed, value, and menu diversity. | English cuisine is often seen as a symbol of tradition and quality, although there is an increasing presence of international cuisines. Handcrafted and high-quality food is generally well-regarded. |